† These authors contributed equally.
§ These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: Peter A. McCullough
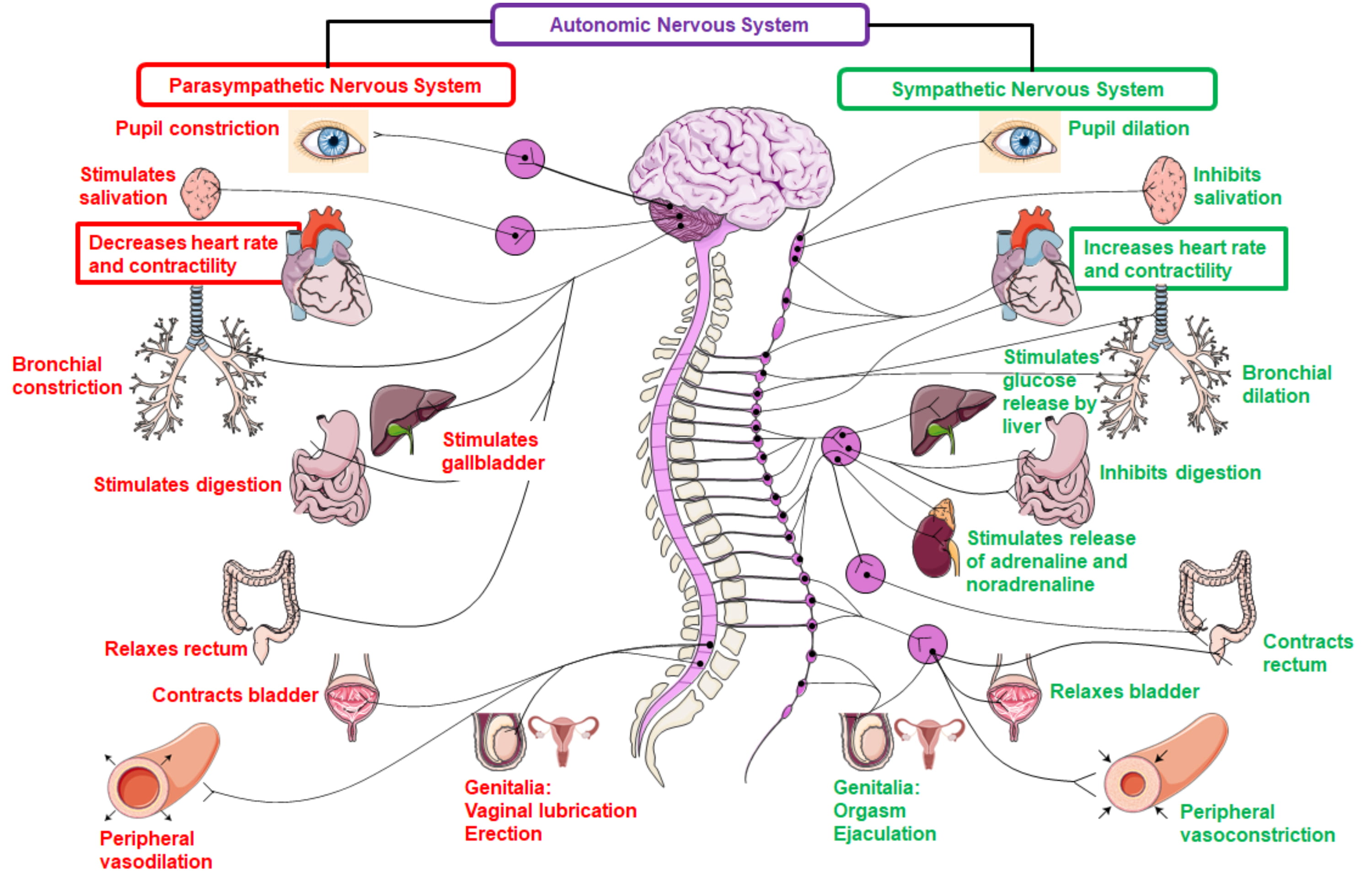
Global diabetes mellitus prevalence is increasing. Metabolic disorders, such as type 2 diabetes, are associated with abnormal cardiac electrophysiology and increased risk of arrhythmias. Patients with both diabetes types (1 and 2) suffer from sudden cardac death (SCD) as a leading cause of mortality. Cardiovascular death is defined as death attributable to cardiovascular disease (CVD) occurring shortly within the symptom onset. This usually arises from life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmias that lead to hemodynamic instability, and subsequent shock and death. A variety of pathways have been suggested that link hypoglycaemia to the development of adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including blood coagulation abnormalities, inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and sympathoadrenal responses. We propose a four-step framework for the optimisation of SCD risk factors in diabetic patients, to include: raising awareness to influence health behaviour, provision of screening programs, use of technology within educational programs to improve patient engagement and effective provision of diabetic community teams.