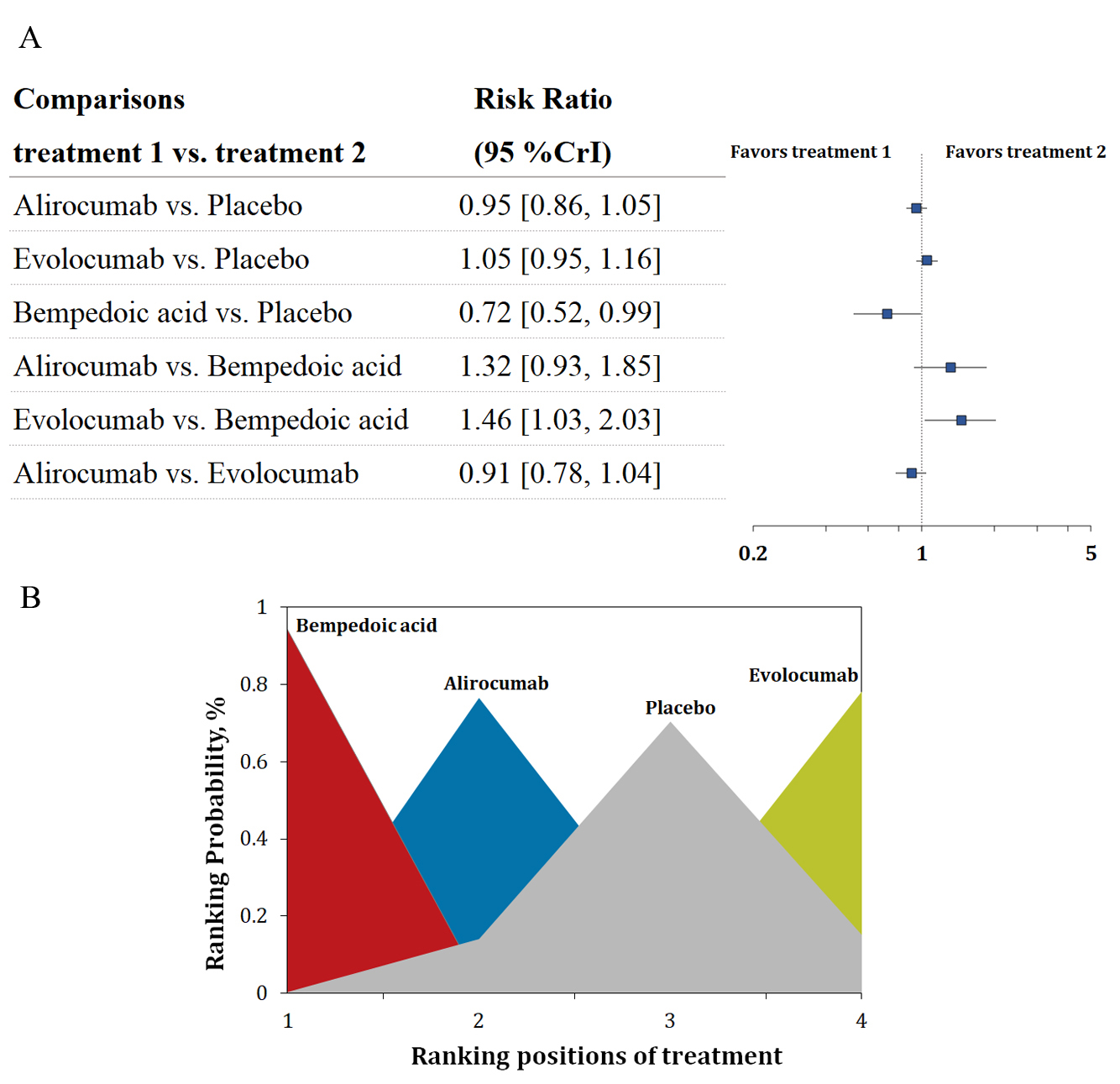
Background: To date, optimal agents for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) reduction in patients with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease are still being explored. Thus, we evaluated the efficiency of novel LDL-C-lowering therapies in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular events. Methods: We included randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that explored the effects of different LDL-C lowering agents including alirocumab, evolocumab, and bempedoic acid in adult patients with cardiovascular disease. Several databases were searched from inception through 2022. The safety endpoint includes new-onset diabetes, serious adverse events, and neurocognitive disorders with at least 1 year of follow-up. The efficacy outcomes included composite adverse cardiovascular outcomes, all-cause death, and cardiovascular death. Results: Seven RCTs comprising 53,106 patients were included in this research. Bempedoic acid ranked first in reducing the risk of new-onset diabetes (risk ratio [RR] 0.72, 95% credible interval [CrI] 0.52–0.99) and risk of the composite cardiovascular outcome (RR 0.75, 95% CrI 0.57–0.99). Meta-regression analysis demonstrated that elevated risk of new-onset diabetes was positively correlated with a significant reduction in LDL-C levels (p = 0.03). All treatment agents were associated with a decreased risk of a composite adverse cardiovascular outcome. Conclusions: The present analysis showed that bempedoic acid ranked first in reducing the risk of a composite cardiovascular outcome. In addition, it ranked first in reducing the risk of new-onset diabetes compared with placebo and evolocumab. Our analysis also suggests that the increased risk of new-onset diabetes might be associated with a reduction in LDL-C levels. Besides, the present analysis found that alirocumab ranked first in decreasing all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality.