- Academic Editor
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
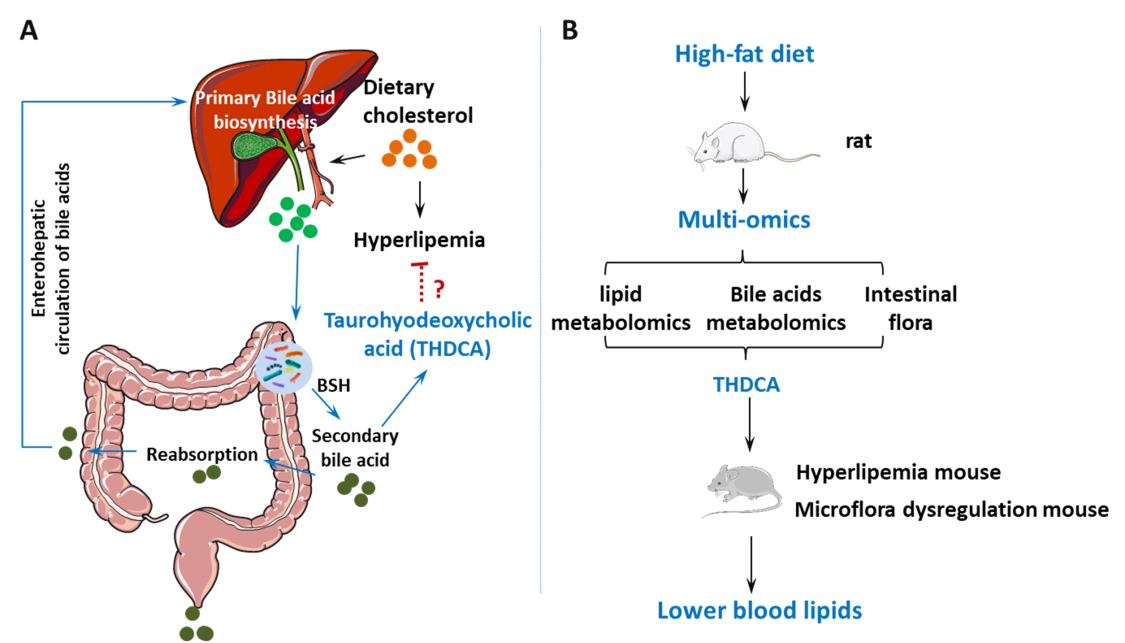
Background: In recent years, with the change in human dietary habits, hyperlipidemia (HLP) has become a common chronic disease. Hyperlipidemia is closely related to the incidence of cardiovascular diseases. Due to the increasing incidence and mortality from cardiovascular diseases, it is imperative to develop new medications for reducing lipid levels. With the aim of discovering new treatment options for hyperlipidemia, we conducted a multi-omics analysis of a potential endogenous bile acid compound. Methods: Two hyperlipidemia models were established by feeding rats and mice with a high-fat diet. Serum and fecal specimens of rats with hyperlipidemia were collected. Through the combined analysis of lipid metabolism sequencing, 16S RNA intestinal flora sequencing, and bile acid targeted metabolism sequencing, taurohyodeoxycholic acid (THDCA) was found to be a potential lipid-lowering compound. A mouse hyperlipidemia model was developed to verify the anti-hyperlipidemia function of THDCA. Results: Analysis of serum lipid metabolites revealed that the synthesis of bile acid was one of the metabolic pathways that showed significant alterations. 16S RNA sequencing of intestinal flora also found that high-fat diet intake greatly influenced both primary and secondary bile acid biosynthesis. Analysis of bile acid metabolites in the serum and liver tissue found that THDCA in the secondary bile acids is a potential biomarker of hyperlipidemia. Verification experiments in mice confirmed the beneficial function of THDCA in lowering abnormal lipid levels induced by a high-fat diet. Conclusions: THDCA has been identified as a biomarker of hyperlipidemia and has shown potential for the treatment of hyperlipidemia.