- Academic Editor
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
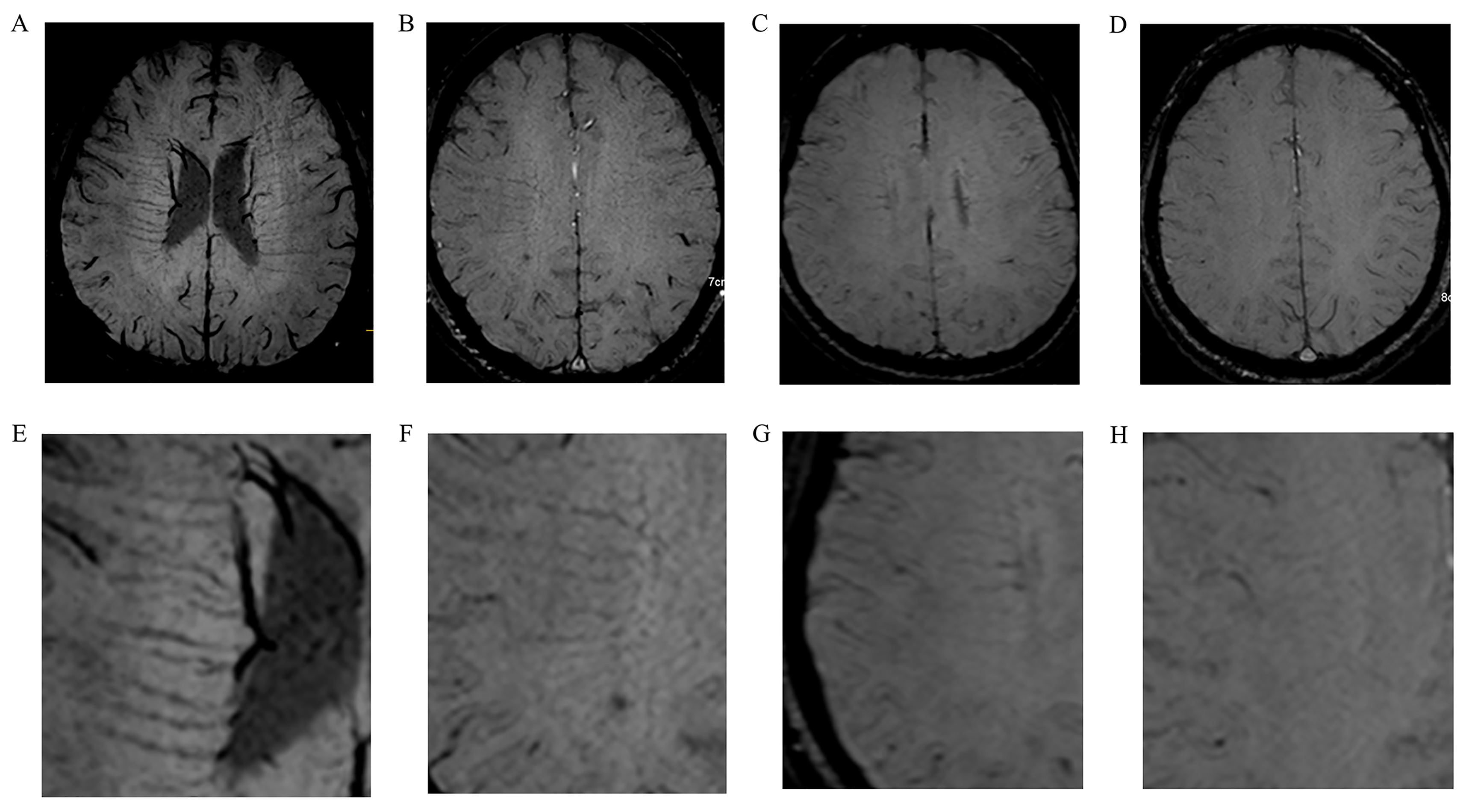
Background: Based on susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) visibility,
deep medullary vein (DMV) scores are related to white matter damage (WMD) in
patients with cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD). However, whether mechanisms
are associated with DMV changes is unclear. We examined extracellular fluid (ECF)
roles in white matter associations between DMV scores and white matter integrity
(WMI) in patients with CSVD. Methods: We examined magnetic resonance
imaging (MRI) and clinical data from 140 patients with CSVD. DMV scores (0–18)
were assigned on SWI according to DMV anatomic regions and signal
continuity/visibility. WMI and ECF volumes were evaluated using free water (FW)
and fractional anisotropy (FA) values by diffusion tensor imaging (DTI).
Results: DMV scores were independently associated with FA after
adjusting for vascular risk factors, age, white matter hyperintensity (WMH)
volume, and CSVD burden [