- Academic Editors
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
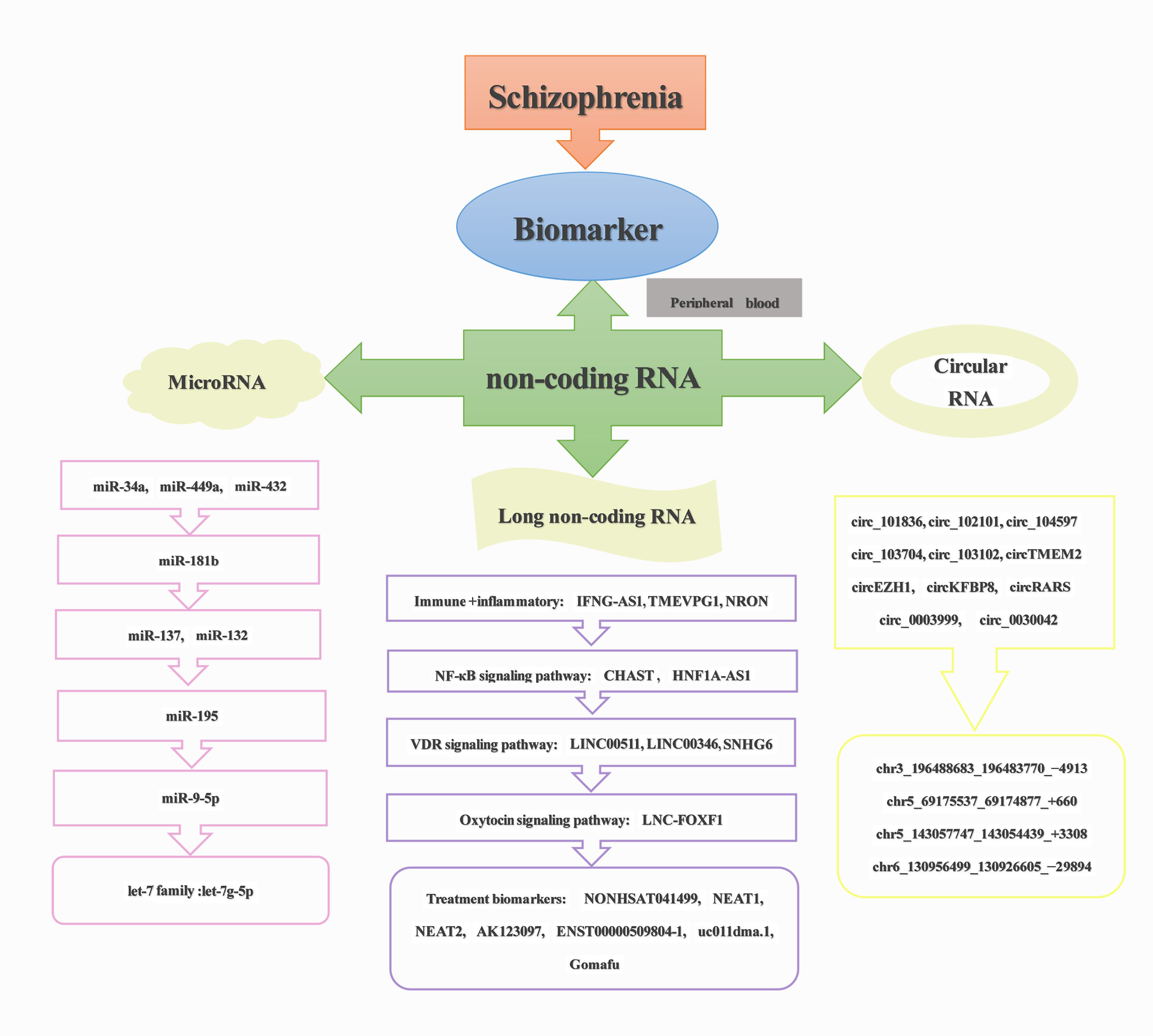
Schizophrenia (SCZ) is a complex and heterogeneous neuropsychiatric disorder that lacks objective diagnostic indicators and the pathogenesis remain unclear. Genetic factors may exert a significant impact on the development of the condition. While obtaining brain tissue for biopsy in the course of adjuvant diagnosis of SCZ patients may not be possible, the collection of peripheral blood is more accessible and easier to implement. In recent years, the development and application of RNA sequencing technology has made seeking biomarkers of SCZ becomes more feasible. There is emerging evidence suggesting that certain non-coding RNAs (ncRNA) are distinctly different in the peripheral blood of SCZ patients and healthy controls. Although the mechanisms remain unclear, these aberrantly expressed ncRNAs may be intimately associated with the onset and development of SCZ and may be of great significance for the diagnosis and treatment of SCZ. Therefore, we reviewed the expression of distinct types of ncRNAs that have been found in the peripheral blood of SCZ patients and explored their potential application as diagnostic biomarkers of SCZ. Differentially expressed ncRNAs in the peripheral blood of SCZ patients could not only serve as potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for SCZ but may also have implications for advancing understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the development of SCZ and elucidating the complex etiology of SCZ. Early diagnostic biomarkers obtained directly from peripheral blood are of great significance for the timely diagnosis and treatment of SCZ. Our review will enhance the comprehension of molecular mechanisms of SCZ and contribute to the identification of promising ncRNAs in peripheral blood for both diagnosis and therapy of SCZ.