- Academic Editor
-
-
-
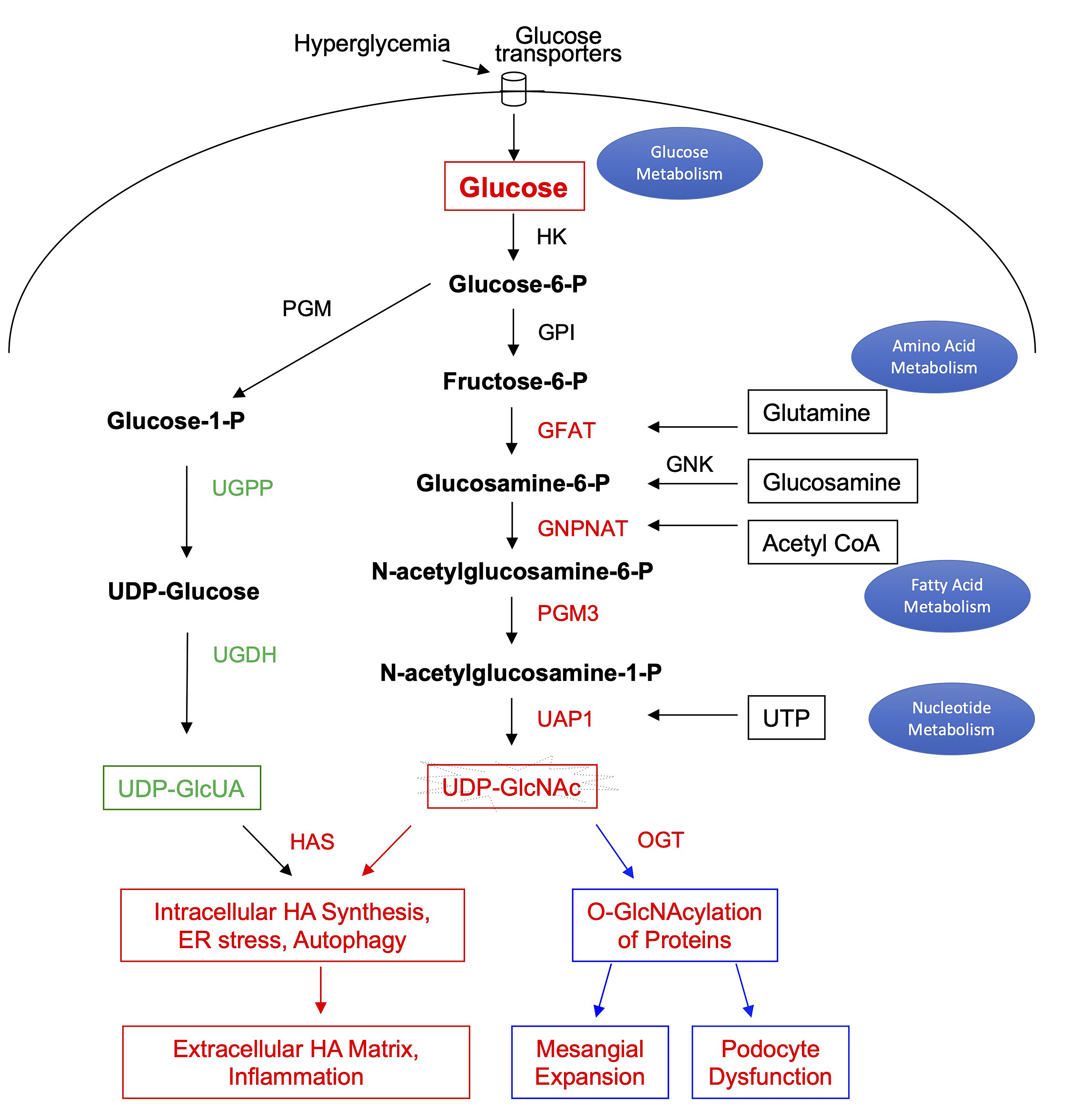
The abnormal intermediate glucose metabolic pathways induced by elevated intracellular glucose levels during hyperglycemia often establish the metabolic abnormality that leads to cellular and structural changes in development and to progression of diabetic pathologies. Glucose toxicity generally refers to the hyperglycemia-induced irreversible cellular dysfunctions over time. These irreversible cellular dysfunctions in diabetic nephropathy include: (1) inflammatory responses, (2) mesangial expansion, and (3) podocyte dysfunction. Using these three cellular events in diabetic nephropathy as examples of glucose toxicity in the diabetic complications, this review focuses on: (1) the molecular and cellular mechanisms associated with the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway that underly glucose toxicity; and (2) the potential therapeutic tools to inhibit hyperglycemia induced pathologies. We propose novel therapeutic strategies that directly shunts intracellular glucose buildup under hyperglycemia by taking advantage of intracellular glucose metabolic pathways to dampen it by normal synthesis and secretion of hyaluronan, and/or by intracellular chondroitin sulfate synthesis and secretion. This could be a useful way to detoxify the glucose toxicity in hyperglycemic dividing cells, which could mitigate the hyperglycemia induced pathologies in diabetes.