-
- Academic Editor
-
-
-
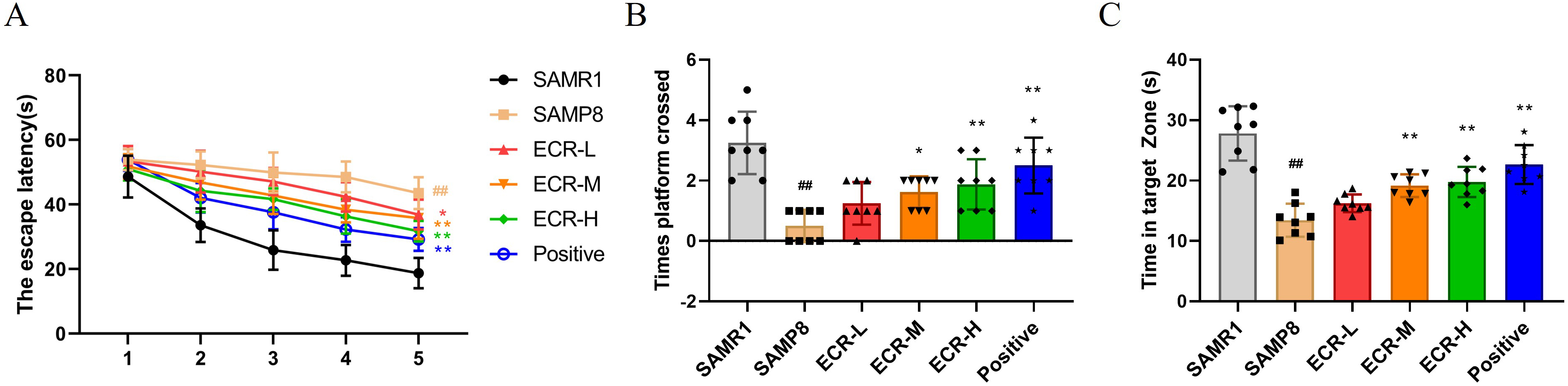
Background: Severe neurological condition like Alzheimer’s disease (AD)
has a significantly negative impact on families and society, wherein there is no
proven cure. As one of the principal active constituents of Achyranthes
bidentata Blume, ecdysterone (ECR) has demonstrated antioxidant and cognitive
dysfunction improvement effects. Nonetheless, the mechanism underlying the
improvement of cognitive dysfunction by ECR remains unclear. This study sought to
ascertain whether ECR may allebviate cognitive impairment by reducing oxidative
stress via activation of the nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) antioxidant system through Akt/GSK3