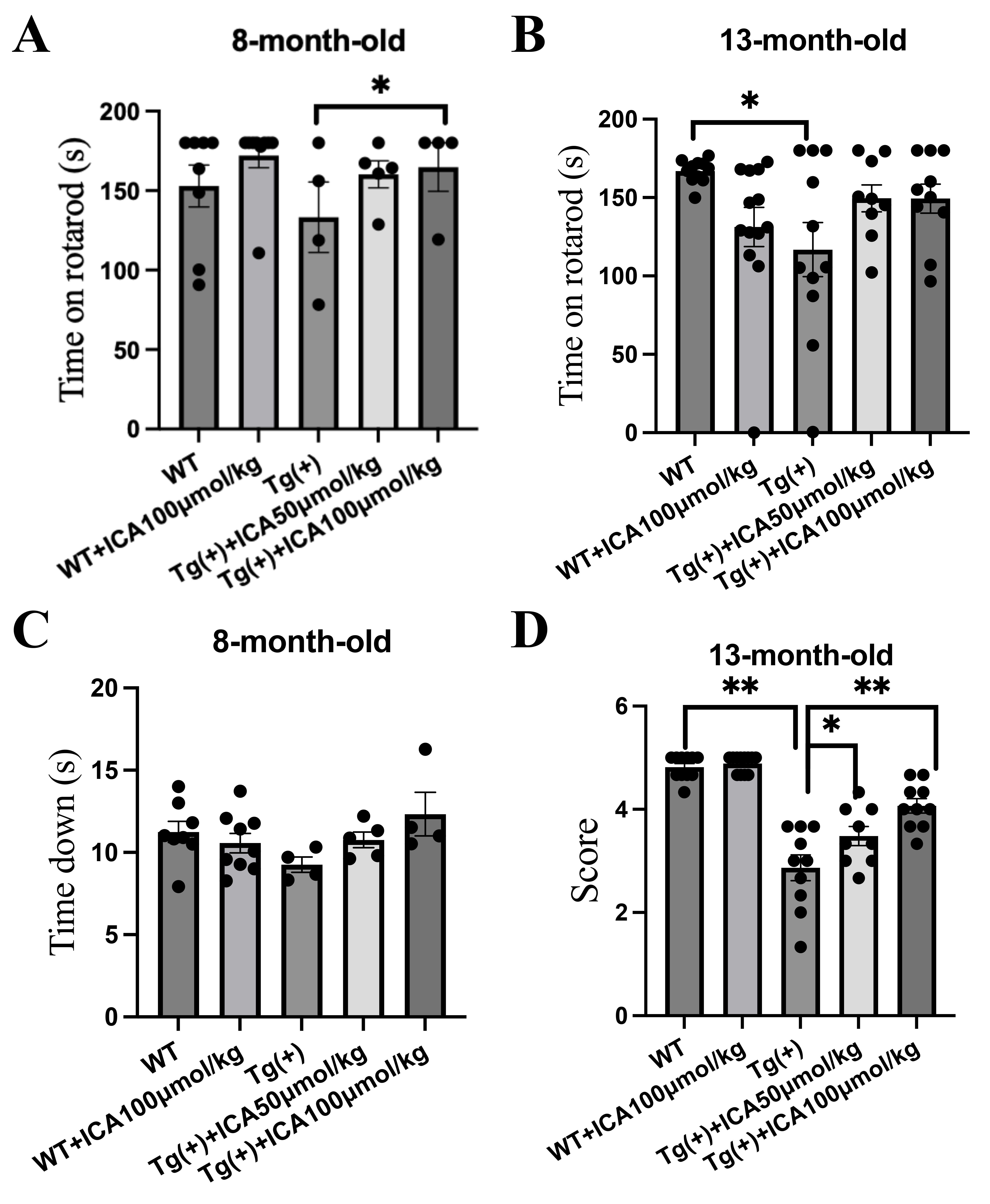
Fig. 1.ICA attenuates behavior dysfunction in young and aged A53T
-synuclein transgenic mice. The rotarod and pole tests were
applied to assess the motor balance and coordination of the A53T Tg mice after
intragastric administration of ICA for 3 months. (A) Time on the rotarod (latency
to fall off the rotarod) of the 8-month-old mice in the rotarod test. (B) Time on
the rotarod of the 13-month-old mice in the rotarod test. (C) Pole test; time
spent climbing down the pole by the 8-month-old mice. (D) Pole test; performance
score for climbing down the pole of mice at 13 months of age. Data are provided
as the mean SEM, n = 4–9 per group (8-month-old mice), n = 9–12 per
group (13-month-old mice). *p 0.05, **p 0.01,
vs. model group. ICA, icariin; SEM, standard error of the mean; Tg (+),
A53T -synuclein transgenic mice; WT, wild type.