- Academic Editor
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
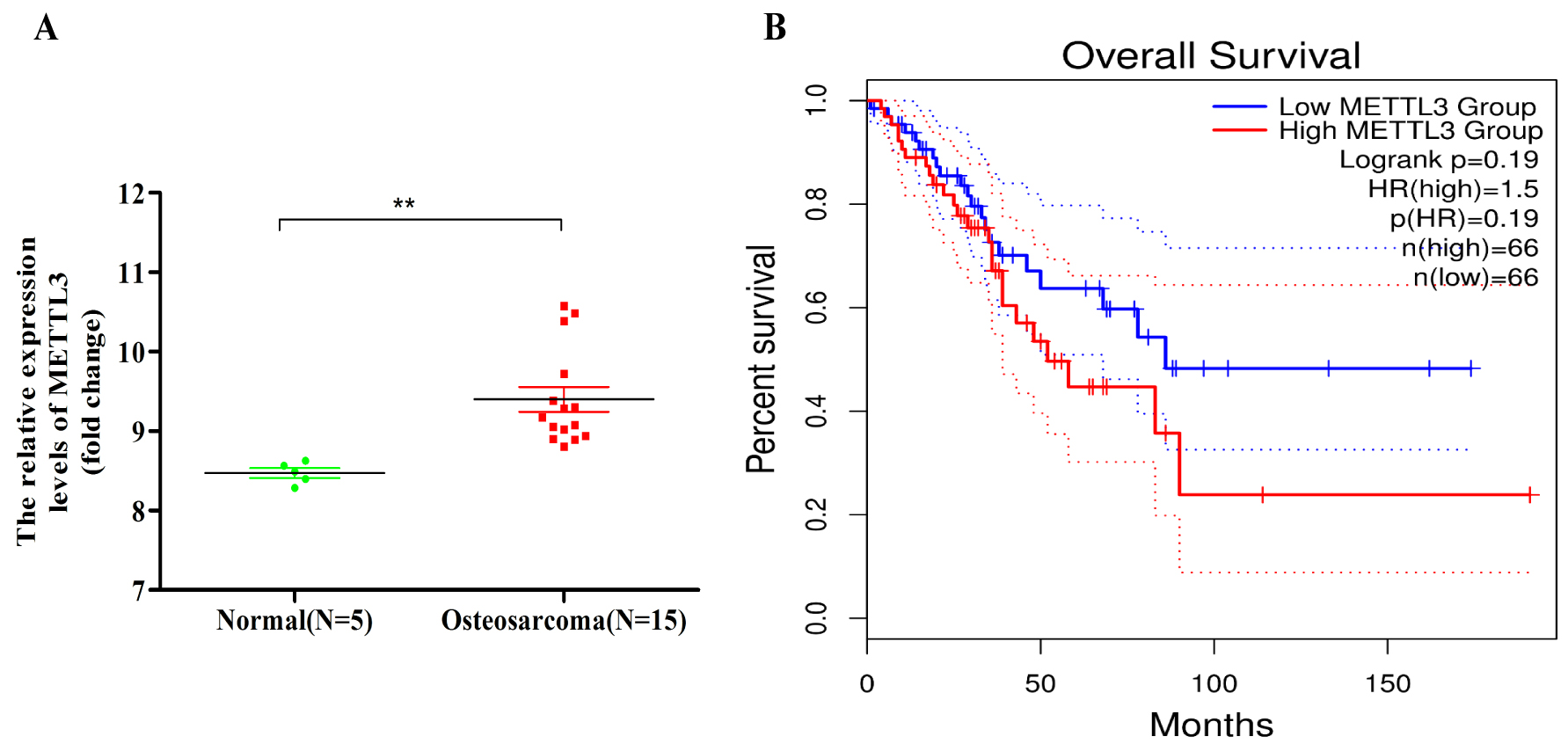
Background: Osteosarcoma cells are prone to metastasis, and the mechanism of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation modification in this process is still unclear. Methylation modification of m6A plays an important role in the development of osteosarcoma, which is mainly due to abnormal expression of enzymes related to methylation modification of m6A, which in turn leads to changes in the methylation level of downstream target genes messenger RNA (mRNA) leading to tumor development. Methods: We analyzed the expression levels of m6A methylation modification-related enzyme genes in GSE12865 whole-genome sequencing data. And we used shRNA (short hairpin RNA) lentiviral interference to interfere with METTL3 (Methyltransferase 3) expression in osteosarcoma cells. We studied the cytological function of METTL3 by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8), flow cytometry, migration and other experiments, and the molecular mechanism of METTL3 by RIP (RNA binding protein immunoprecipitation), Western blot and other experiments. Results: We found that METTL3 is abnormally highly expressed in osteosarcoma and interferes with METTL3 expression in osteosarcoma cells to inhibit metastasis, proliferation, and apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells. We subsequently found that METTL3 binds to the mRNA of CBX4 (chromobox homolog 4), a very important regulatory protein in osteosarcoma metastasis, and METTL3 regulates the mRNA and protein expression of CBX4. Further studies revealed that METTL3 inhibited metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by regulating CBX4. METTL3 has been found to be involved in osteosarcoma cells metastasis by CBX4 affecting the protein expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2), MMP9, E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin associated with osteosarcoma cells metastasis. Conclusions: These results suggest that the combined action of METTL3 and CBX4 plays an important role in the regulation of metastasis of osteosarcoma, and therefore, the METTL3-CBX4 axis pathway may be a new potential therapeutic target for osteosarcoma.